Module 2, midterm simulation test¶
This is the second QCB MidTerm exam provided in December 2020.
In the following, you will find the complete text and the solutions for the practical exercises. Please, refer to Alessandro Romanel for any comment on the theoretical part.
Theoretical part¶
Exercise 1¶
Given a list 𝐿 of 𝑛≥3 integer elements, please compute the asymptotic computational complexity of the following function, explaining your reasoning.
[1]:
def my_fun(L):
for i in range(3, len(L)):
k = 0
R = L[i]
tmp = []
while k < 3:
if k % 2 == 1:
R = R - L[k]
else:
R = R + L[k]
k += 1
tmp.append(R)
return sum(tmp)
Exercise 2¶
What is the topological sorting of a directed acyclic graph (DAG)? Briefly describe an algorithm to compute it and provide a possible topological view of the following DAG.
Practical part¶
Exercise 3¶
Guess-sort is a sorting algorithm working as follows:
Pick two indices
iandjat random; ifa[i] > a[j], then swap them.Repeat until the input is sorted.
Implement the GuessSort class by extending the provided SortingAlgorithm class. Test it on a random array of 500 elements and check its correctness. Then, analyze the time complexity of this algorithm.
[2]:
class SortingAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, data, verbose = True):
self.data = data
self.comparisons = 0
self.operations = 0
self.verbose = verbose
def getData(self):
return self.data
def getOperations(self):
return self.operations
def getComparisons(self):
return self.comparisons
def sort(self):
raise NotImplementedError
sa = SortingAlgorithm([])
print(sa)
sa.sort()
<__main__.SortingAlgorithm object at 0x7facc31e0c40>
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[2], line 22
20 sa = SortingAlgorithm([])
21 print(sa)
---> 22 sa.sort()
Cell In[2], line 18, in SortingAlgorithm.sort(self)
17 def sort(self):
---> 18 raise NotImplementedError
NotImplementedError:
Show/Hide Implementation
Exercise 4¶
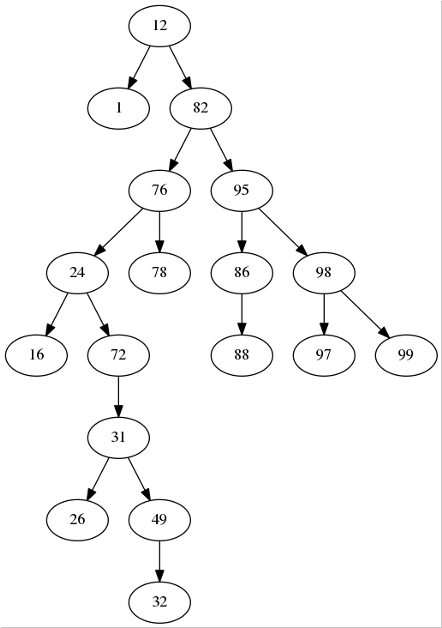
Given a binary search tree as the one provided in the file BST.py, implement the missing function search_interval(a, b) that given two values a and b, finds all values between a and b in the tree, returning them in an ordered data structure. For instance, calling search_interval(24, 33) on the following tree should return: [24, 26, 31, 32].

[4]:
class BinaryTree:
def __init__(self, value):
self.__data = value
self.__right = None
self.__left = None
self.__parent = None
self.__depth = 0
def getDepth(self):
return self.__depth
def setDepth(self, newdepth):
self.__depth = newdepth
def getValue(self):
return self.__data
def setValue(self, newValue):
self.__data = newValue
def getParent(self):
return self.__parent
def setParent(self, tree):
self.__parent = tree
def getRight(self):
return self.__right
def getLeft(self):
return self.__left
def insertRight(self, tree):
if self.__right == None:
self.__right = tree
tree.setParent(self)
tree.setDepth(self.getDepth() + 1)
def insertLeft(self, tree):
if self.__left == None:
self.__left = tree
tree.setDepth(self.getDepth() + 1)
tree.setParent(self)
def deleteRight(self):
self.__right = None
def deleteLeft(self):
self.__left = None
def inOrderDFS(self):
ret = []
if self != None:
r = self.getRight()
l = self.getLeft()
if l != None:
ret.extend(l.inOrderDFS())
ret.append(self.getValue())
if r != None:
ret.extend(r.inOrderDFS())
return ret
def search_interval(self, a, b):
raise NotImplementedError
def createBST(intList):
BST = None
if len(intList) > 0:
BST = BinaryTree(intList[0])
for el in intList[1:]:
cur_el = BST
alreadyPresent = False
prev_el = None
while cur_el != None:
prev_el = cur_el
cv = cur_el.getValue()
if cv > el:
cur_el = cur_el.getLeft()
elif cv < el:
cur_el = cur_el.getRight()
else:
# cv == el (el is already present)
# not allowed by rule c, so skip it
alreadyPresent = True
#print("El {} already present".format(el))
break
if not alreadyPresent:
node = BinaryTree(el)
node.setParent(prev_el)
if prev_el.getValue() > el:
prev_el.insertLeft(node)
else:
prev_el.insertRight(node)
return BST
def printTree(root):
cur = root
#each element is a node and a depth
#depth is used to format prints (with tabs)
nodes = [(cur,0)]
tabs = ""
lev = 0
while len(nodes) >0:
cur, lev = nodes.pop(-1)
if cur.getRight() != None:
print ("{}{} (r)-> {}".format("\t"*lev,
cur.getValue(),
cur.getRight().getValue()))
nodes.append((cur.getRight(), lev+1))
if cur.getLeft() != None:
print ("{}{} (l)-> {}".format("\t"*lev,
cur.getValue(),
cur.getLeft().getValue()))
nodes.append((cur.getLeft(), lev+1))
if __name__ == "__main__":
import random
inList = []
for i in range(1000):
inList.append(random.randint(0,1000))
#printTree(createBST(inList[:20])) # to test tree creation...
BST = createBST(inList)
sorted = BST.search_interval(24, 33)
print("Elements between 24 and 33 in the BST:")
print(sorted)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NotImplementedError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[4], line 125
121 #printTree(createBST(inList[:20])) # to test tree creation...
123 BST = createBST(inList)
--> 125 sorted = BST.search_interval(24, 33)
126 print("Elements between 24 and 33 in the BST:")
127 print(sorted)
Cell In[4], line 58, in BinaryTree.search_interval(self, a, b)
57 def search_interval(self, a, b):
---> 58 raise NotImplementedError
NotImplementedError:
Show/Hide Implementation